ABSTRACT
Pulsed electric field (PEF) use short electric pulses to preserve the food. It is suitable for preserving liquid and semi-liquid foods, removing micro-organisms and producing functional constituents. PEF has not yet been used in Europe on industrial scale although it has been used in the US for orange juice and it has considerable potential for improving quality and taste of pasteurized foods compared with traditional preservation techniques.
Pulsed electric field (PEF) processing is a novel, non-thermal preservation method that has the potential to produce foods with excellent sensory and nutritional quality and shelf-life. High intensity pulsed electric field (HIPEF) processing involves the application of pulses of high voltage (typically 20 – 80 kV/cm) to foods placed between 2 electrodes. PEF treatment is conducted at ambient, sub-ambient, or slightly above ambient temperature for less than 1 s, achieved by multiple short duration pulses typically less than 5 μs and energy loss due to heating of foods as well as undesirable changes in the sensory properties of the food is minimized.
PEF technology has been presented as advantageous in comparison to, for instance, heat treatments, because it kills microorganisms while better maintaining the original colour, flavour, texture, and nutritional value of the unprocessed food. PEF technology involves the application of pulses of high voltage to liquid or semi-solid foods placed between two electrodes. Most PEF studies have focused on PEF treatments effect on the microbial activation in milk, milk products, egg products, juices and other liquid foods.
OBJECTIVE
- Pulsed electric field (PEF) used short electric pulses to preserve the food.
- It is suitable for preserving liquid and semi-liquid foods, removing harmful micro-organisms and producing functional constituents.
- The main objective of PEF processing is to inactivate microorganisms present while minimizing changes in physical, sensory and nutritional properties.
- PEF technology involves the application of pulses of high voltage to liquid or semi-solid foods placed between two electrodes.
- HIPEF consists of several components including a power source, capacitor tank, a switch, treatment chamber, voltage current and temperature sensors and aseptic packaging equipment.
- Generation of different voltage waveforms in PEF: exponential pulses, square pulses, bipolar pulses and oscillatory pulses.
EXISTING SYSTEM
- In pulsed ohmic heating systems, another technique for microbial inactivation in which the electric pulses with much lower amplitudes are applied, the use of titanium and platinized titanium electrodes showed superior performance compared with stainless steel and graphite ones.
- In commercially available systems for PEF processing, production of the required voltage pulses uses either conventional Blumlein generators or generators like those found in radar power sources.
- For the indirect inactivation of pathogenic organisms, plasma treatment of liquids before application allows for the accumulation of RONS and reduction in pH.
- For earlier research of streamers in water pulsed high voltage sources with stacked transmission lines in combination with a spark gap have been used.
PROPOSED SYSTEM
- Pulsed electric fields PEF is a non-thermal method of food preservation that uses short pulses of electricity for microbial inactivation and causes minimal detrimental effect on food quality attributes.
- PEF technology aims to offer consumers high-quality foods. For food quality attributes, PEF technology is considered superior to traditional thermal processing methods because it avoids or greatly reduces detrimental changes in the sensory and physical properties of foods.
- Our system of the PEF technology is the application of short pulses of high electric fields with duration of microseconds micro- to milliseconds and intensity in the order of 10- 80 kV/cm.
- The processing time is calculated by multiplying the number of pulses times with effective pulse duration.
- The process is based on pulsed electrical currents delivered to a product placed between a set of electrodes; the distance between electrodes is termed as the treatment gap of the PEF chamber.
MOTIVATION
- The use of an external electrical field for a few microseconds induces local structural changes and a rapid breakdown of the cell membrane.
- Based on this phenomenon, called electroporation, many applications of high intensity pulsed electric fields (HIPEF) have been studied in the last decade.
- This process of reversible pore formation must be controlled to maintain viability of the organisms during the application of the PEF.
- Due to the reversible permeabilization, the cells repair their membranes through resealing the electro pores immediately after the PEF treatment.
- At higher treatment intensity PEF can be utilized for the inactivation of microorganisms by an irreversible breakdown of the cell membrane.
SCOPE
Among all emerging nonthermal technologies, high intensity pulsed electric fields (PEF) is one of the most appealing technologies due to its short treatment times and reduced heating effects with respect to other technologies.
PEF is commonly understood as a nonthermal food preservation technology that involves the discharge of high voltage electric pulses (up to70 kV/cm) into the food product, which is placed between two electrodes for a few microseconds.
BLOCK DIAGRAM
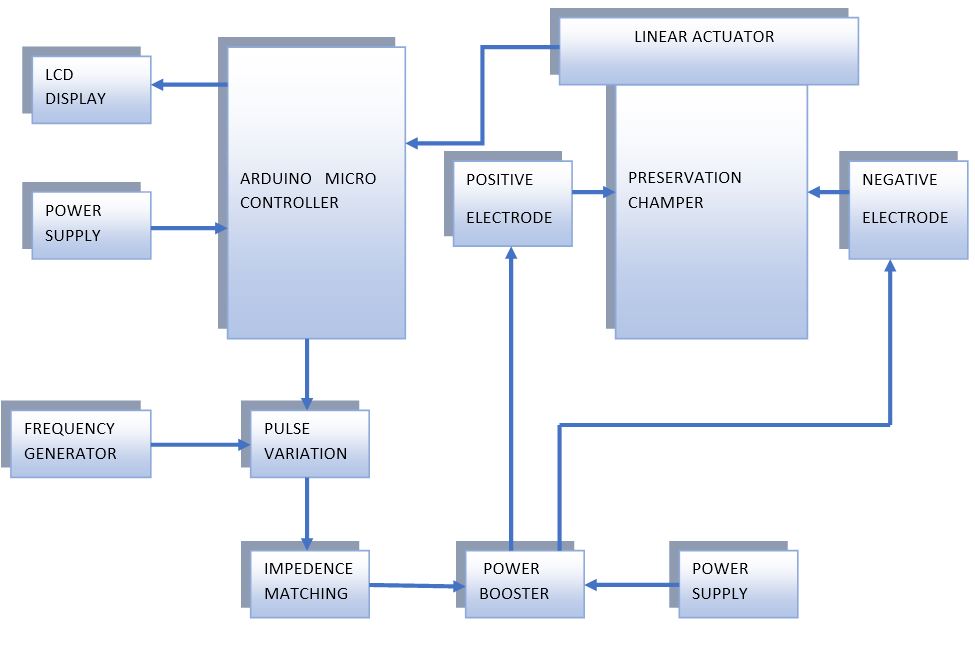
Hardware Requirements
- Power Supply
- Microcontroller
- Lcd display
- Electrodes
- Actuator
- Frequency Generator
Software Requirements
- Embedded C
- Arduino IDE
Conclusion:
PEF inactivates vegetative micro-organisms including yeasts, spoilage micro-organisms and pathogens, and it can be used to pasteurize fluids such as juices, milk and soups without using additives. This technology can substitute for conventional heat pasteurization or it can operate at room temperature to retain quality and heat-sensitive vitamins. PEF can be used as continuous process but, after processing, products have to be packaged hygienically and kept cool during storage. Using some of antimicrobial substances prolongs the shelf life of foods within pulsed electric fields. An application of PEF for food preservation provides the tremendous potential to preserve high quality products at lower temperatures and short residence time to retain the fresh-like character and nutritional value of the products.